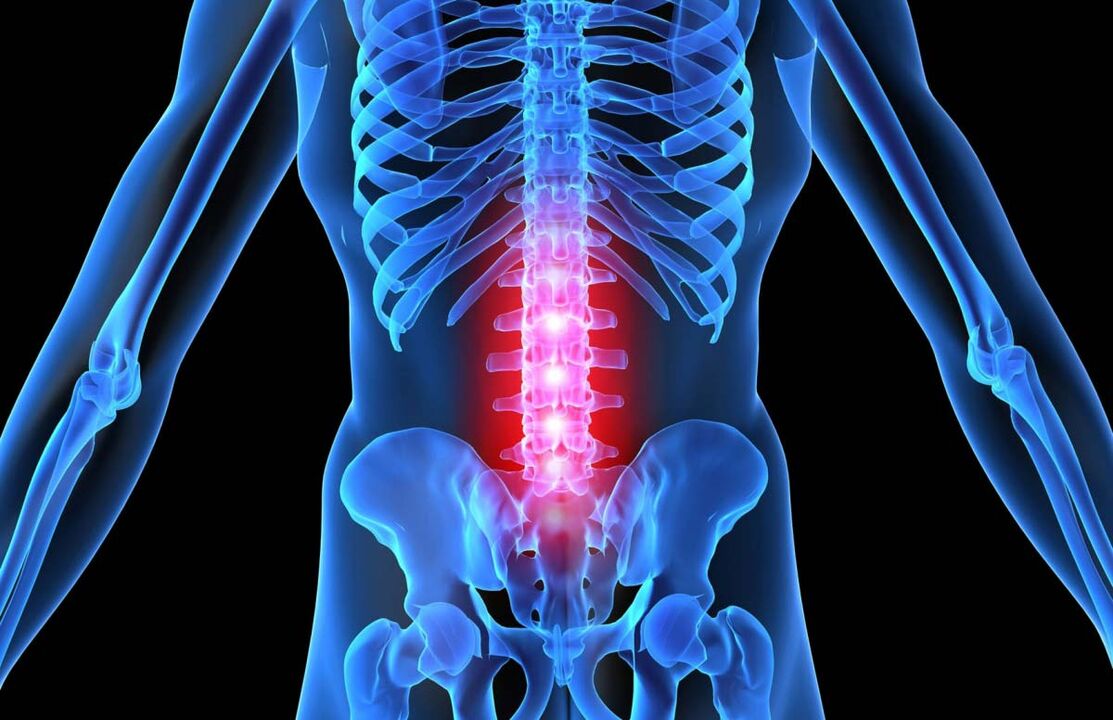
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is expressed by dystrophic damage to the aforementioned part of the back, damage to the nucleus of the intervertebral discs, and deformity of the intervertebral joints in the background of ligament abnormalities. In this pathological process, in the later stages of the disease, the blood vessels are involved and even the nervous system.
What is lumbar osteochondrosis?
Lumbar spine osteochondrosis is one of the most common musculoskeletal disorders in the world. Irregular pain syndromes in the designated area are experienced by up to sixty percent of the population, and one in ten residents is diagnosed with osteochondrosis in one form or another, with nearly half of the cases due to defeat of the lumbar and sacral regions.
This disease quickly "rejuvenates", sometimes even in adolescents and children - it is a sedentary lifestyle / work failure, excessive passion for computer games, lack of full physical activity - sports and active games are supplanted by long stays on the PC -n.
However, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine can also occur due to excessive stress, especially if it is exacerbated by being overweight. The problem is caused by poor posture as well as back injuries, non-compliance with the daily diet and regular malnutrition.
Negative factors that accelerate the development of the preconditions for the appearance of this type of osteochondrosis are chronic sleep deprivation, stress, slowing down the body's metabolic processes. A separate category for professional athletes.
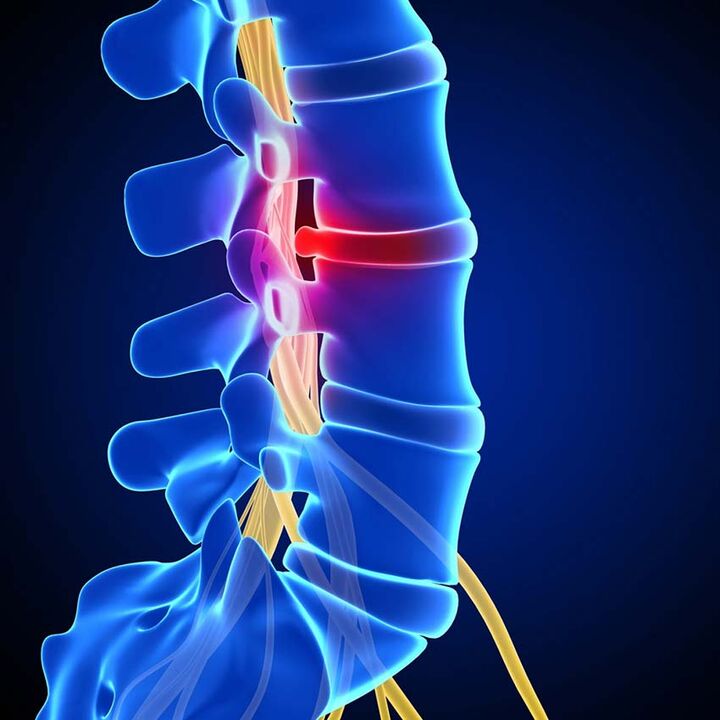
Many experts note that in some cases, osteochondrosis is a consequence of a person’s genetic predisposition: intervertebral discs, however, have a loose porous structure and are destroyed very rapidly by pathogenic negative factors, and the disease progresses. they are diagnosed quickly and only at a late, sometimes irreversible stage.
A special risk group includes people with rheumatoid arthritis as well as spondyloarthritis, which provoke the development of the above-mentioned autoimmune disease and complicate its course.
First signs. Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
The main symptoms of the disease described above are, of course, pain syndrome. Prolonged painful pain in the lumbar region of moderate intensity can be replaced by a strong "lumbago" after active physical work or an uncomfortable position. Usually, in the supine position, the pain syndrome is virtually absent or disappears completely.
With aggravation as well as severe physical exertion, hypothermia, or non-physiological movements, the pain syndrome loses its localization in the lower back and goes to the pelvic region and even the legs.
In detail, the patient develops the following pathologies:
Compression of nerve roots
- Root lesions L 1–2: pain in local localizations, loss of sensation in the inner and groin of the thigh.
- L-5 lesion: lumbar pain in the lower back, irradiation of the thumb.
- S-1 lesion: pain and numbness in the thigh, outer surface of the foot, temporary disappearance of reflexes in the sole and lower leg.
Arterial lesion
Local damage to the DH artery causes:
- Regular numbness of the lower leg / buttocks.
- Loss of sensitivity in the genital area.
- In rare cases, loss of pelvic motor function.
Vascular compression ischemia
Violation of the blood supply to the spinal cord and other peripheral structures leads to "thinning" of the structure of the intervertebral plates and, accordingly, to abnormal mobility of the spine, the development of osteophytes and neoarthrosis.
Compression myelopathy
Narrowing of the spinal canal causes intermittent paroxysmal weakness in the limbs, painful "lumbar" syndrome in the lower back, with retraction to the back of the thigh. In light of this, hypotrophy / hypotension of the gastrocnemius / gluteal muscles, disappearance of the plantar, anal and Achilles reflexes, and paresis of the foot develop.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine

It is possible and necessary to treat the disease. Of course, in this case, only complex therapy, which aims to reduce the symptoms of the autoimmune disease, restore the structure of the spine, and prevent the problem from recurring, will help.
Complex therapy for the above disease includes:
- Taking medications.
- Blockade injections.
- Gymnastics and training therapy.
- Massage and manual therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
Preparations for lumbar osteochondrosis
- Analgesics.
- Restoration of chondroprotectors.
- Vitamins. Optimal - Group B.
- Injections. Anesthetics, cartilage regenerators and normalizers of blood microcirculation.
- Local funds. Corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
It is an important element of spinal rehabilitation. Each procedure is individually developed to relieve pain and muscle cramps, normalize blood circulation, and restore the work of intervertebral discs.
Massage for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Massage is an essential part of the complex therapy of the disease. It helps to relax and train the lower back muscles, triggers the cartilage tissue recovery process and relieves pain.
Most commonly, therapeutic, acupressure, hardware, vacuum, and connective tissue massage are used for the disease described above.
Physiotherapy
Generally, physiotherapy is prescribed to patients with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine only during the remission phase of the disease, after overcoming the period of exacerbation of the problem.
Modern and classic techniques:
- Acupuncture. Exposure of posterior acupuncture points with special needles.
- Stretching. The classic technique is to stretch the spine on a massage-pulling couch by a trained chiropractor.
- Electrophoresis. It has been a known, complex, non-operational method of influencing external problem areas since the 1960s.
- Traction decompression. Automated hardware spine tensioning in a special medical complex.
- Shockwave therapy. Use of infrared waves for the treatment of osteochondrosis.
- Osteopathy. A complex technique that combines elements of chiropractic, massage, and therapeutic orthopedics.
- Magnetopuncture. The direct effect of the alternating magnetic field on the spine.
- Laser stabbing. Treatment of acupuncture points with induced radiation.
- Electrical stimulation. Application of small alternating currents in the affected areas.
Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
After complex treatment and physiotherapy, supportive therapy is needed for a long time: during this period, the spine is still weakened and needs support. In addition, prevention is intended to prevent the occurrence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. Main activities:
- Regular, balanced exercise, preferably under the supervision of a qualified podiatrist.
- Normalization of body weight: often the overweight person is an aggravating factor that influences the development of osteochondrosis.
- Dietary correction. A regular diet should include foods rich in elements such as calcium and magnesium. In this case, it is worth excluding overly fatty and unhealthy foods, as well as other foods that do not fall within the definition of a healthy diet.
- Rejection of bad habits. Alcohol and smoking increase all the destructive processes in the body, including the occurrence of osteochondrosis.
- Proper posture. Be sure to monitor your posture, especially if your work involves a constant computer stay or other sedentary activity. Also pay attention to your child - how and for how long you sit. Normal correct posture will prevent the appearance of scoliosis and, accordingly, osteochondrosis in the future.
- Use appropriate shoes, clothing and accessories to avoid wearing weights regularly. The wrong shoe, the heavy bag, acts as a loader on the shoulder - all of these factors sometimes have a decisive influence on the development of destructive processes in the spine.
Question answer
What is the pain of this type of osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is characterized by several types of pain. First, these are localized discomforts in the lumbar region that last for a long time and increase significantly with the person’s motor activity and physical work. This type of pain disappears when the body is in a horizontal position for at least 15-20 minutes.
If the disease is exacerbated by hypothermia, prolonged intense physiological stress, or sharp "everting" movements, in addition to the aforementioned background pain, there is also a "shooting" effect that localizes in the pelvic region and radiates to the lower. limbs.
Is exercise useful in this osteochondrosis?
Physiotherapy therapeutic gymnastics makes it possible to confirm the good effect of the complex therapy of the disease, to partially develop the intervertebral components of the joints, and to relax / train the muscles of the lumbar region. In addition, proper regular massage will help get rid of the unpleasant pain associated with osteochondrosis.
The specific set and list of exercises, the number of approaches and the frequency of the exercises will be worked out for you by your doctor: he will consider the current stage of the disease, the possible list of contraindications and limitations, the patient's condition and suggest methods for practicing exercise therapy.

























